الوصف
Cables play a critical role in construction and building infrastructure. From supplying electricity to communication and safety systems, cables ensure a building functions efficiently and safely. Without proper cables and installation planning, construction projects face serious risks, including electrical failures, fire hazards, and system breakdowns. A clear understanding of cable types, material options, installation standards, and performance attributes helps homeowners, engineers, and contractors make informed decisions for long-term reliability.
Construction cables differ from standard household wires because they must withstand environmental, mechanical, and performance stress. Whether installing power distribution systems, data networks, fire alarm systems, or grounding protections, selecting the right cable ensures safety and function across the entire structure.
What Are Construction Cables?
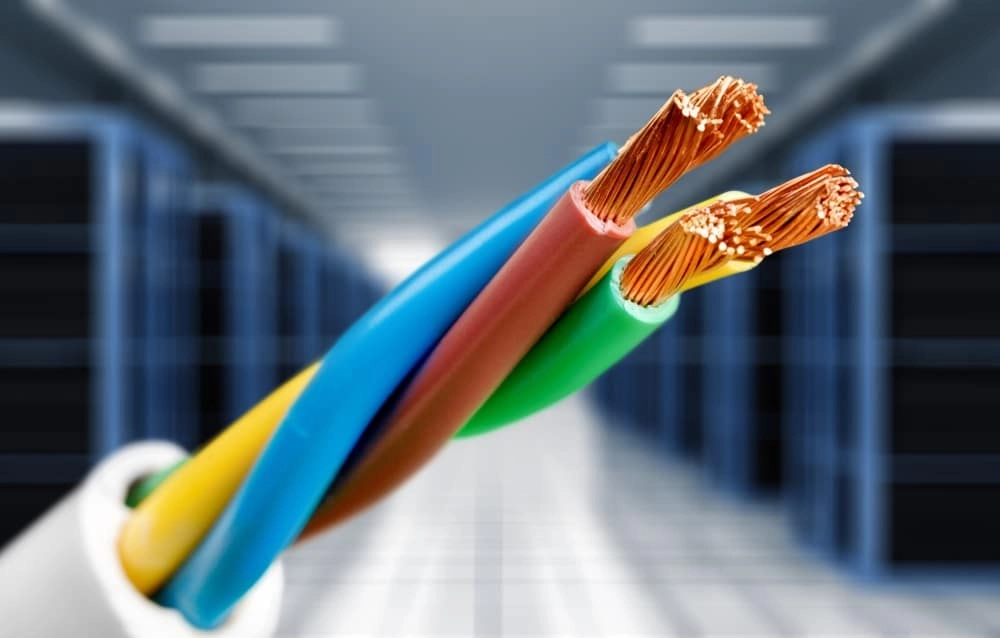
Construction cables refer to electrical and communication conductors specifically designed to be used in building projects. These cables support key infrastructure operations such as lighting distribution, appliance power, HVAC systems, internet networks, emergency systems, and grounding safety. Their design varies based on factors like voltage rating, insulation material, fire-resistance capability, and application environment. Construction cables must meet strict national and international standards for safety and durability, ensuring consistent performance throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Importance of Cables in Building Projects
Cables ensure safe and stable power transfer, signaling, and communication throughout a building. They protect occupants by preventing electrical leakage and reducing fire risk through proper insulation and fire-retardant features. High-quality cables improve electrical efficiency, reduce voltage drop, and enhance equipment lifespan. In modern smart buildings, advanced cables also support automation, networking, and high-speed data requirements. Using poor-quality cables or installing them incorrectly leads to frequent breakdowns, expensive repairs, and dangerous hazards.
Types of Construction Cables
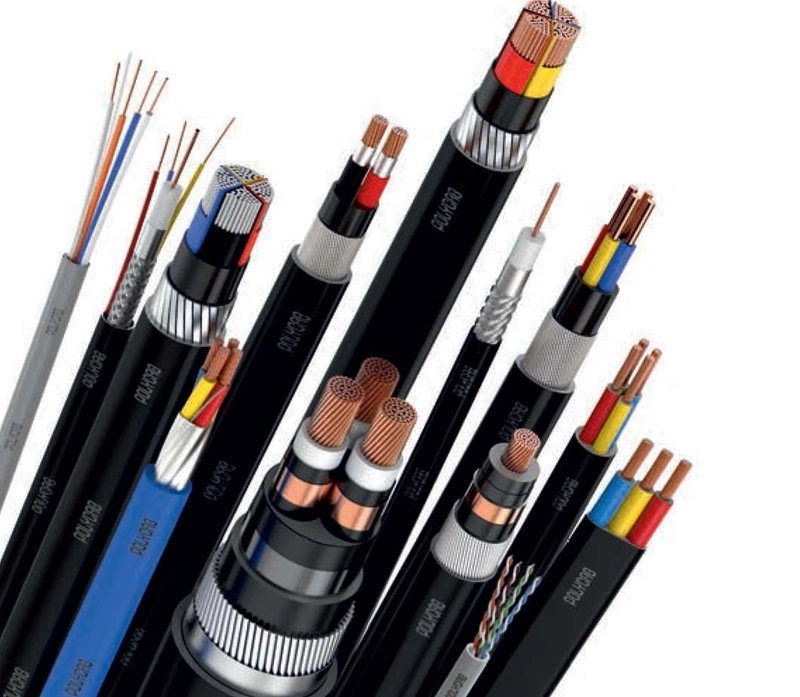

Construction projects require multiple cable types to support different systems. Each cable type carries distinct features suitable for specific conditions and uses. Understanding these ensures proper selection and long-term safety of electrical infrastructure. Common categories include power cables, control cables, communication cables, fire-resistant cables, and grounding conductors. The selection depends on load requirements, environmental exposure, installation pathways, and expected lifespan in the construction environment.
Power Distribution Cables
Power distribution cables are designed to transfer electricity from the main supply panel to circuits throughout the building. These cables handle low-, medium-, or high-voltage loads depending on project scale. Their insulation materials vary, commonly including PVC or XLPE for safety and thermal stability. Power cables must be chosen based on current capacity, conductor size, and insulation thickness to prevent overheating and energy loss. Proper power cable selection ensures stable delivery to lighting systems, appliances, and heavy electrical devices in residential and commercial buildings.
Low Voltage and Data Cables
Low-voltage and data cables connect communication networks, security systems, and smart building devices. These include Ethernet cables, fiber optic cables, telephone wires, alarm system cables, and CCTV-compatible wiring. Their primary role is transmitting data signals with accuracy and speed. Insulation quality protects signals from electromagnetic interference and external noise. Modern construction projects often require advanced low-voltage solutions to support automation features and high-bandwidth communication needs in both residential and office buildings.
Fire-Resistant and Fire-Retardant Cables
Fire-resistant and fire-retardant cables support safety systems by continuing to operate during fire emergencies. These cables ensure critical functions like fire alarms, emergency lighting, smoke detectors, and communication systems remain active during high-temperature exposure. Fire-resistant cables maintain circuit integrity for a specified duration, while fire-retardant types limit the fire spread by preventing flame propagation. Building safety codes often mandate their use, especially in high-occupancy structures and industrial facilities.
Control and Instrumentation Cables
Control and instrumentation cables transmit signals to control electrical devices and automation systems. They are widely used in industrial buildings, HVAC systems, and building automation. The conductors and shielding designs help resist interference, ensuring precise data transfer and accurate operation. These cables enhance energy efficiency and building performance by enabling remote monitoring, machinery control, and system diagnostics.
Grounding and Earthing Cables
Grounding cables safeguard buildings by providing a safe path for fault currents. They protect occupants and electrical devices from electric shock and overvoltage during electrical faults or lightning strikes. Grounding cables use tinned or bare copper due to conductivity and corrosion resistance. Proper grounding system installation is essential to comply with building safety standards and electrical regulations.
Materials Used in Construction Cables
Construction cables are manufactured using different conductor and insulation materials to ensure optimal performance under various building conditions. The most common conductors are copper and aluminum, each offering unique benefits in terms of conductivity, flexibility, and cost. Insulation materials such as PVC, XLPE, rubber, and fire-resistant compounds are selected based on environmental exposure, heat tolerance, and safety requirements. Choosing the correct material combination ensures long-term durability, safety, and efficiency in electrical systems within buildings.
Copper Cables
Copper cables are widely used in construction due to their superior conductivity, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. Copper supports high electrical loads with minimal energy loss, making it ideal for power distribution, grounding, and communication systems. Its mechanical strength allows easy installation in tight spaces, conduits, and complex building layouts. Copper cables also offer long service life and reliability, especially in environments requiring stable electrical performance and minimal maintenance.
Aluminum Cables
Aluminum cables provide a lightweight and cost-effective alternative to copper cables, especially for large-scale building and industrial installations. Although aluminum is less conductive than copper, it can be manufactured with larger cross-sections to compensate for electrical capacity. Aluminum cables are commonly used in main feeder circuits, overhead installations, and projects where weight reduction is important. Proper installation and connection techniques are essential to prevent oxidation and maintain efficient performance.
PVC Insulation
PVC insulation is one of the most common protective layers used in construction cables. It offers strong resistance to moisture, abrasion, and chemical exposure, making it suitable for indoor wiring, conduit systems, and protected outdoor applications. PVC-insulated cables are cost-effective and meet essential building safety standards. However, they may not be ideal for environments requiring high heat tolerance, as excessive temperatures can affect insulation quality over time.
XLPE Insulation
XLPE insulation provides enhanced heat resistance, electrical strength, and long-term stability compared to PVC. It is commonly used in medium- and high-voltage cables, underground installations, and high-demand circuits within buildings. XLPE insulation performs efficiently in harsh environmental conditions and resists chemical and moisture penetration. It supports improved current-carrying capacity, making it a preferred option for modern energy-efficient electrical systems.
Standards and Certifications in Cable Manufacturing
Cables used in construction must comply with recognized safety and performance standards. These standards guarantee the cable’s suitability for installation in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Certifications ensure the cable can withstand environmental stress, electrical load, and emergency conditions like fire or overload. Standards bodies may vary by region, but their role remains consistent—protecting people, property, and electrical infrastructure from hazards.
International Cable Standards
International electrical cable standards establish safety and quality benchmarks for cable manufacturing and performance. Organizations like IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) define rules for cable insulation, conductor quality, voltage rating, fire resistance, and operational capacity. Following these guidelines ensures that cables perform reliably in varied building conditions and comply with global best practices.
Regional and Local Standards
Each country may have local regulations governing cable installation in buildings. Examples include NEC (National Electrical Code) in the United States, BS standards in the United Kingdom, and EU fire-safety rules in Europe. These standards ensure cables meet the specific safety requirements and building regulations of each region. Compliance prevents legal issues, ensures building approval, and improves long-term system performance.
Applications of Construction Cables
Construction cables serve multiple roles throughout the electrical and communication infrastructure of a building. They power lights, outlets, air-conditioning systems, elevators, and electronic devices. They also support communication networks, security systems, emergency equipment, and automation functions. Proper cable selection ensures reliable energy distribution, uninterrupted data transmission, and safe performance of critical systems within residential towers, offices, industrial units, and commercial buildings.
Residential Buildings
In residential construction, cables are used for lighting systems, power outlets, appliance circuits, and home automation systems. Safe and efficient wiring ensures comfort and convenience for homeowners. Residential building codes dictate permissible cable types, installation methods, and safety requirements. Low-voltage cables for internet, telephone, smart doorbells, and security systems are also essential for modern homes.
Commercial Buildings
Commercial buildings require high-capacity cables to support large electrical loads such as HVAC units, lifts, office machines, and lighting networks. Structured cabling systems manage data, communication, and security functions across multiple floors and network zones. Fire-resistant cables support emergency systems like exit lighting, alarms, and smoke control units. Commercial installations demand high-quality materials to ensure safety and operational stability.
Industrial and Infrastructure Projects
Industrial and infrastructure environments use specialized cables designed for heavy electrical loads, mechanical stress, and extreme conditions. These cables support motors, machinery, and industrial automation systems in factories and warehouses. Advanced shielding protects signal integrity in sensitive environments like control rooms and data centers. Durable insulation materials protect cables from oil, vibration, and environmental damage.
Installation Guidelines for Construction Cables
Proper cable installation is essential for operational efficiency and safety. Planning includes circuit design, load calculation, cable routing, and compliance with electrical codes. Installation must ensure safe distances from heat sources, sharp surfaces, and moisture while maintaining appropriate spacing for ventilation. Correct termination techniques, grounding, and protective conduits are critical for ensuring cable integrity and longevity in buildings.
Safety Considerations
Electrical safety during cable installation prevents hazards such as shock, short circuits, and fire incidents. Safety rules enforce correct wire sizing, circuit protection, and proper fastening to avoid loose connections or insulation damage. Professionals must follow lock-out tag-out procedures, use insulated tools, and verify circuit de-energization before work. High-risk areas require fire-resistant cable selections and secure insulation to ensure compliance with building safety codes.
Common Installation Methods
Construction cables can be installed through various methods depending on building design and load requirements. Typical approaches include conduit systems, cable trays, trunking, and direct burial for underground power lines. Conduits protect cables from physical damage and moisture, while trays support large cable bundles in commercial and industrial structures. Proper routing prevents overheating, interference, and mechanical strain. Installation techniques must comply with electrical codes to guarantee safe operation throughout the building’s lifespan.
Underground vs Surface Installation
Underground installation protects cables from external damage and environmental exposure, but it requires specialized insulation, waterproofing, and proper soil preparation. Surface installation uses conduits, ducts, and trunking mounted on walls or ceilings, making maintenance and troubleshooting easier. Both methods must account for load capacity, ventilation, environmental safety, and structural considerations to ensure long-term reliability. The choice depends on project scale, accessibility needs, and environmental safety factors.
Maintenance of Cables
Maintaining construction cables ensures sustained performance and prevents failures that can interrupt building operations. Regular inspections identify insulation wear, loose connections, and corrosion early. Maintenance includes thermal scanning, load testing, and routine tightening of terminals and joints. Preventive strategies improve energy efficiency, reduce repair costs, and enhance safety by minimizing fire and electrical risks. Proper labeling and documentation support efficient troubleshooting and upgrades over time.
Signs of Cable Wear and Damage
Common signs of cable deterioration include discoloration, cracking insulation, reduced flexibility, and excessive heat generation. Frequent breaker trips or power loss may indicate cable overload or internal breakdown. Corrosion, moisture intrusion, and pest damage can also affect cable condition. Identifying these issues early avoids system failures and ensures reliable building function. Damaged cables must be replaced promptly to prevent further hazards.
Preventive Measures
Preventive maintenance includes scheduled inspections, thermal monitoring, testing insulation resistance, and ensuring secure cable fastening. Using high-quality fittings, protective conduits, and moisture barriers extends cable lifespan. Correct load distribution and adequate ventilation reduce overheating risks. Training technicians on safe cable handling and installation minimizes errors and enhances long-term safety for building occupants and systems.
Purchase Guide for Cables
Purchasing construction cables requires evaluating electrical specifications, environmental conditions, project needs, and compliance with standards. Buyers should consider voltage rating, insulation type, conductor material, and fire-safety requirements. Consulting certified electrical engineers ensures optimal cable selection. Comparing manufacturers, warranties, and certification labels guarantees long-lasting and safe installations in both residential and commercial construction projects.
Factors to Consider When Buying Cables
Key factors include conductor size, insulation material, temperature rating, and installation environment. Load calculations determine cable gauge, preventing overheating and energy loss. Brands that follow international safety standards offer more reliable performance. Buyers should also review documentation, test reports, and labeling for voltage capacity, flame resistance, and compliance with local electrical regulations.
Recommended Cable Brands
Reputable cable manufacturers offer certified products with guaranteed performance and safety standards. These brands typically provide durable conductors, fire-resistant materials, and comprehensive testing results. Choosing established brands reduces long-term maintenance needs and lowers the risk of electrical faults. Project scale, budget, and application type influence brand selection in construction projects.
Cable Price Guide
Cable prices depend on material type, conductor size, insulation quality, voltage rating, and brand reputation. Market conditions and global metal prices also affect cost, particularly for copper-based cables. Bulk purchasing often reduces unit prices for commercial or industrial projects. Evaluating lifecycle performance and warranty coverage helps balance budget and reliability.
Price Factors in Construction Cables
Conductor material significantly influences price, with copper being more expensive than aluminum due to higher conductivity and durability. XLPE insulation generally costs more than PVC due to enhanced thermal resistance and long service performance. Cable size, fire-resistant properties, and shielding also impact pricing. Installation and labor costs must be included in total project budgets.
Market Pricing Trends
Cable pricing can vary based on fluctuations in raw material markets, especially metals. Seasonal construction demands may also affect availability and supplier pricing. Long-term contracts and wholesale purchases provide more stability in large-scale construction projects. Monitoring supplier reliability and delivery capacity ensures timely procurement and reduces project delays.
Where to Buy Construction Cables
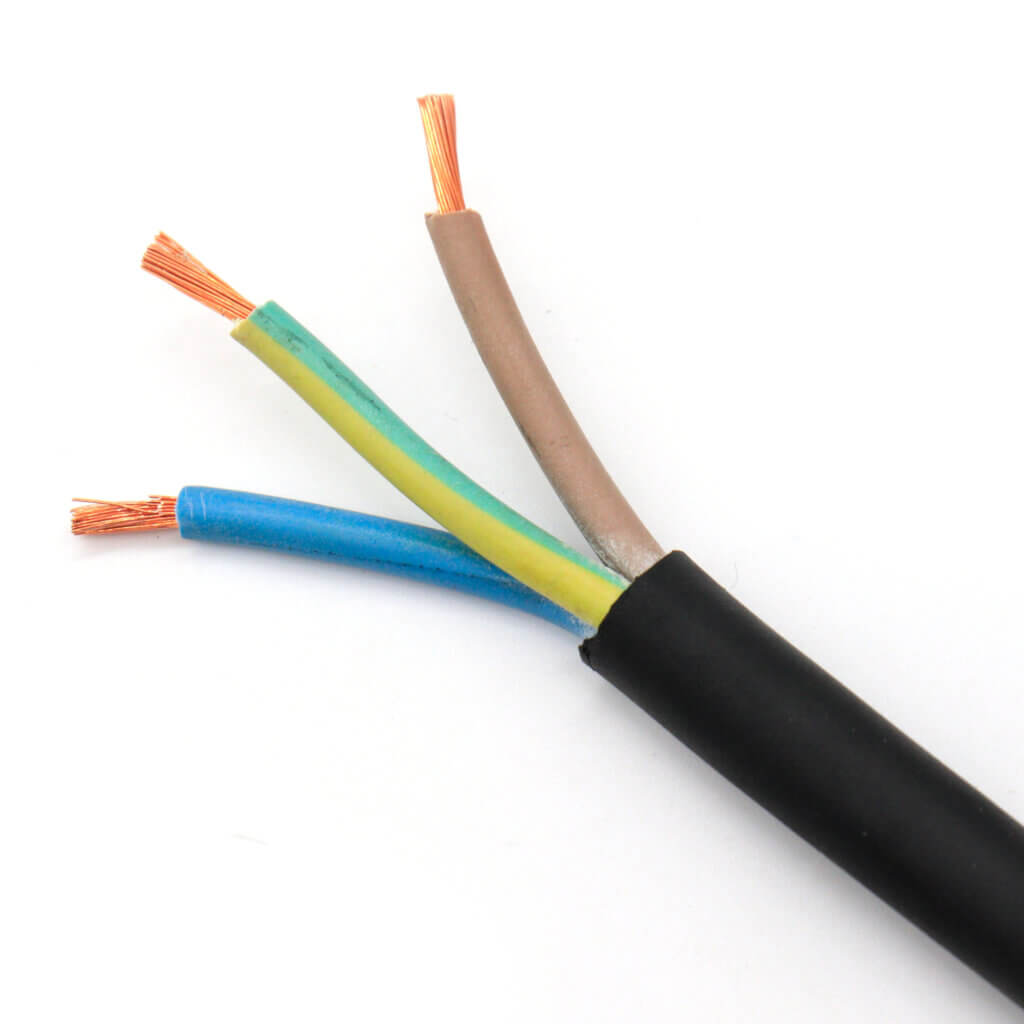
Construction cables can be purchased through authorized electrical distributors, certified manufacturers, and specialized electrical supply stores. Buyers may also find certified products through online construction marketplaces and supply chain networks. It is important to verify product authenticity and ensure compliance with safety certifications before purchasing. Professional consultation helps avoid incorrect cable selection and installation errors.
Trusted Suppliers and Distribution Channels
Authorized dealers offer quality assurance, warranty support, and technical assistance to ensure appropriate cable selection for building applications. Local distributors provide fast delivery and accessibility for emergency replacements and continued projects. Online suppliers offer variety and competitive pricing but require extra verification to avoid counterfeit products. Choosing reliable vendors ensures consistent cable quality and availability.
Installation and Safety Certifications
Certified cable installation ensures that wiring systems comply with building standards and safety codes. Certified electricians follow approved wiring methods, ensure proper grounding, and use correct tools and materials. Safety certification includes visual inspections, electrical testing, and documentation to prove compliance. Certification protects property owners, reduces risk of failure, and ensures system longevity. Municipal authorities may require inspection reports before issuing building completion approvals.
Why Certification Matters
Certification ensures that cables are installed correctly to prevent fire, shock hazards, and performance failures. It demonstrates compliance with local and international regulations. Certification also protects building owners legally by proving that electrical systems were installed professionally and tested for safety. In modern construction, certified systems also increase property value and insurance acceptance.
Environmental Considerations for Construction Cables
Environmental factors influence cable performance and durability. Moisture, temperature fluctuations, chemical exposure, and UV radiation can degrade insulation and conductor integrity if not addressed. Construction projects must consider eco-friendly materials, energy efficiency, and recycling practices when choosing cables. Awareness of environmental impact supports sustainable and resilient infrastructure development.
Sustainable Cable Materials
Some cable manufacturers produce eco-friendly insulation and sheathing materials that reduce environmental footprints. These include halogen-free compounds that minimize toxin release during fire events. Environmentally responsible cable products support green building certifications and long-term sustainability goals. Recycling copper and aluminum conductors reduces resource consumption and supports circular-economy initiatives.
Heat and Moisture Resistance
Cables installed in humid or high-temperature environments require special insulation designed to withstand moisture and heat exposure. Proper moisture sealing and protective conduit installation prevent corrosion and insulation degradation. Buildings in coastal or industrial areas benefit from specially coated cables that resist chemical effects and corrosion. Proper selection ensures continuous operation in demanding conditions.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Project
Selecting the right cable requires technical understanding and planning. Load requirements, building size, installation environment, and system purpose influence cable selection. Consulting electrical engineers ensures correct sizing, insulation type, and safety rating. Choosing cables that exceed minimum code requirements improves safety and longevity. Each building system, from lighting to communication networks, demands a specific cable configuration for optimal performance.
Expert Advice for Builders and Contractors
Builders and contractors should involve certified electricians early in planning to avoid costly rewiring. Technical professionals calculate loads, plan wiring routes, and recommend cable types based on codes. Using updated standards and certified materials ensures that installations comply with legal requirements, delivering efficient and safe power distribution and communication systems throughout the property.
Purchase Recommendations
Purchasing cables requires sourcing from trusted and certified suppliers. Buyers should request test certificates, warranty coverage, and regulatory compliance documents. Comparing brand performance history, customer support, and product testing ensures investment in reliable infrastructure. Always confirm that cable specifications match project requirements and local electrical guidelines.
Quality vs Budget Considerations
Balancing budget and quality is essential in cable procurement. Lower prices may compromise insulation, conductor purity, fire performance, and durability. Investing in certified, high-quality cables reduces long-term risk and maintenance expenses. In critical installations, spending slightly more on premium brands increases system reliability and safety, protecting buildings and occupants.
FAQs
What are construction cables used for?
Construction cables are used for power distribution, communication networks, grounding, and control systems in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. They support lighting, appliances, data transfer, and safety systems throughout the structure.
Which is better for buildings, copper or aluminum cable?
Copper offers superior conductivity, durability, and reliability, making it ideal for most building applications. Aluminum is a cost-effective choice for large feeders and industrial installations where weight and price are concerns.
Are fire-resistant cables necessary?
Yes, fire-resistant cables are essential in emergency systems such as fire alarms, emergency lighting, and ventilation control. They maintain power supply during fire events and support safe building evacuation and emergency response.
How often should building cables be inspected?
Routine inspections should be performed annually, with more frequent checks for older systems or heavy-load environments. Thermal scans and insulation testing help identify early signs of wear or overheating.
Where can I buy construction cables?
Construction cables can be purchased from authorized distributors, certified manufacturers, and reputable online industrial supply platforms. Always verify compliance certificates and product authenticity before purchase.



المراجعات
لا توجد مراجعات بعد.