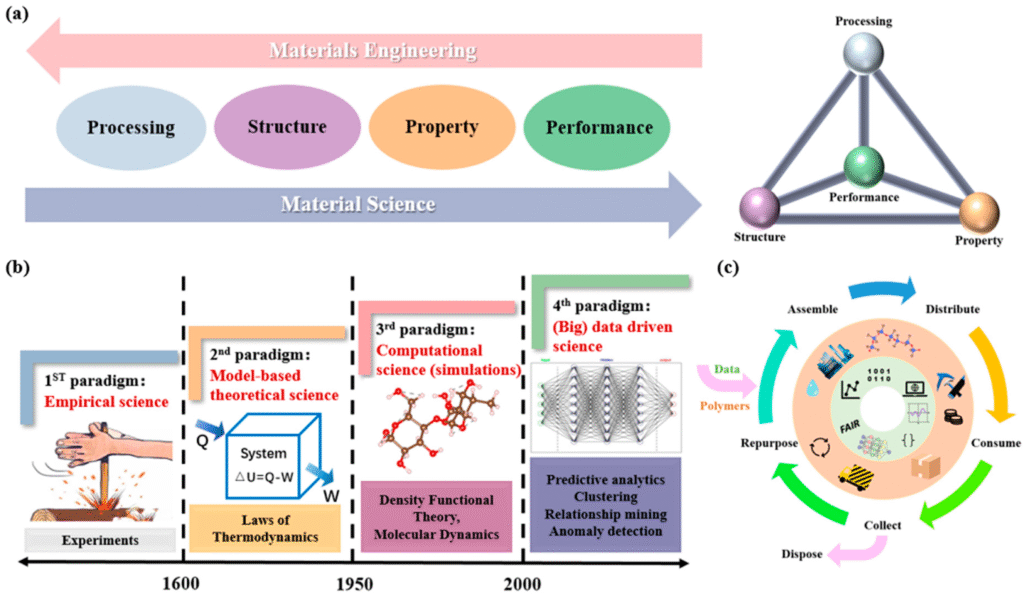
The phrase Inside the Polymer Lifecycle: Engineering Tomorrow’s Materials Today is more than a scientific concept; it represents a global transformation in materials science. In today’s rapidly advancing world, polymers shape industries from healthcare to aerospace. Understanding their lifecycle and engineering smarter materials not only drives innovation but also empowers sustainable progress. This guide explores every stage of the polymer lifecycle, the science behind tomorrow’s advanced materials, and how engineering breakthroughs redefine performance, sustainability, and industrial efficiency.
>>> bic cable
Why the Polymer Lifecycle Matters
Polymers are the backbone of modern technology. They appear in medical implants, smartphones, packaging, automobiles, and renewable energy systems. As industries evolve, polymer engineering must balance three critical goals:
-
Exceptional performance
-
Cost efficiency
-
Environmental sustainability
Today’s innovators focus on Inside the Polymer Lifecycle: Engineering Tomorrow’s Materials Today, prioritizing design, processing, usage, and recycling in a circular economy. From molecular design to degradation and reuse, each phase is crucial for creating the next generation of smart, strong, and eco-friendly materials.
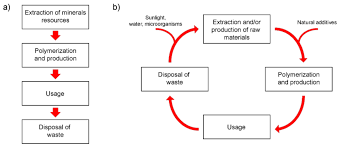
What Is the Polymer Lifecycle?
The polymer lifecycle refers to the complete journey of a polymer material, including:
-
Raw material extraction
-
Polymer synthesis
-
Processing and manufacturing
-
Product use
-
End-of-life recycling or disposal
A modern perspective transforms this into a closed-loop lifecycle, where raw materials are reused rather than wasted.
The Future of Polymer Engineering
Toward Sustainable Innovation
The scientific community is aggressively moving toward biodegradable plastics, bio-based polymers, and recyclable composites. The shift aligns with global climate goals and consumer demand for greener products.
Key drivers shaping tomorrow’s polymers:
-
Circular economy initiatives
-
Strict environmental regulations
-
Growth in biotechnology and nanotechnology
-
Industry-academic research collaboration
-
AI-driven materials discovery
Companies embracing lifecycle-focused polymer engineering gain competitive advantages, reduce waste, and strengthen brand trust.
Stages of the Polymer Lifecycle
1. Polymer Design and Synthesis
At the molecular level, materials engineers tailor polymer structure for specific functions:
-
Strength and durability
-
Resistance to temperature and chemicals
-
Electrical conductivity
-
Flexibility and transparency
Popular Synthesis Techniques
-
Addition polymerization
-
Condensation polymerization
-
Ring-opening polymerization
Advanced methods like AI-assisted molecular modeling accelerate discovery and reduce trial-and-error experimentation.
2. Material Processing and Manufacturing
Once synthesized, polymers undergo processing to become usable products.
Common techniques:
-
Injection molding
-
Extrusion
-
3D printing
-
Blow molding
-
Compression molding
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) now plays a transformative role in custom polymer structures for medical, industrial, and aerospace applications.
3. Performance in Real-World Applications
Polymers serve diverse industries:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Prosthetics, implants, drug delivery |
| Electronics | Circuit boards, casings, cables |
| Automotive | Lightweight body panels, fuel-efficient parts |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine blades, solar films |
| Packaging | Food-safe containers, protective layers |
Tomorrow’s materials emphasize lighter weight, improved thermal stability, and enhanced recyclability without sacrificing strength.
4. Degradation, Waste Management & Recycling
Traditional petroleum-based plastics degrade slowly and pollute ecosystems. Engineers now explore:
-
Enzymatic and chemical recycling
-
Biodegradable polymers
-
Compostable materials
-
Thermal depolymerization
Circular engineering ensures materials can be reused, reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
>>> bic stone
Types of Advanced Polymers Shaping the Future
Bio-Based Polymers
Derived from renewable resources like corn, algae, and sugarcane.
Smart Polymers
Change shape or properties in response to stimuli (temperature, pH, light).
Nanocomposite Polymers
Nanomaterials enhance conductivity, strength, and chemical resistance.
Self-Healing Polymers
Repair micro-cracks automatically, extending product lifespan.
Recyclable Thermoplastics
Engineered for multiple reuse cycles without performance loss.
Benefits of Lifecycle-Driven Polymer Design
Key Advantages
-
Reduced environmental impact
-
Longer product life
-
Enhanced performance and efficiency
-
Cost savings in manufacturing
-
Compliance with global sustainability regulations
Industry Example
Automotive manufacturers increasingly replace metals with engineered polymers to:
-
Reduce weight
-
Improve fuel efficiency
-
Increase corrosion resistance
Challenges and Limitations
Despite breakthroughs, challenges exist:
-
High cost of advanced materials
-
Limited large-scale recycling infrastructure
-
Knowledge gap in emerging markets
-
Need for cross-industry collaboration
Continuous education, policy support, and investment are essential for accelerating adoption.
Future Trends in Polymer Science
| Trend | Impact |
|---|---|
| AI-assisted materials engineering | Faster material discovery |
| Green chemistry | Low-emission manufacturing |
| Biodegradable & compostable plastics | Waste reduction |
| Polymer batteries | Next-gen clean energy |
| Light-activated healing polymers | Longer-lasting industrial equipment |
The future rests on sustainable engineering and responsible innovation.
Organizations seeking superior performance, regulatory compliance, and environmental leadership must invest in lifecycle-engineered polymer solutions. Whether you are a manufacturer, researcher, or startup founder, adopting Inside the Polymer Lifecycle: Engineering Tomorrow’s Materials Today is the pathway to long-term competitive value.
For expert consultation or industry partnership inquiries, contact our polymer engineering team and unlock the future of advanced materials.
>>> bic tile
Lifecycle Data Analytics: Measuring Polymer Performance for the Future
Modern polymer engineering does not rely solely on laboratory experiments. Lifecycle data analytics now plays a central role in decision-making and performance enhancement. By combining machine learning models, environmental simulations, and field performance tracking, engineers gather actionable insights such as:
-
Durability under real-world stress conditions
-
Degradation rate in natural and industrial environments
-
Optimal recycling paths and economic feasibility
-
Environmental footprint across supply chains
-
Energy consumption during manufacturing
This data-driven approach aligns with the core concept of Inside the Polymer Lifecycle: Engineering Tomorrow’s Materials Today, empowering companies to design materials that perform better, last longer, and return to the lifecycle with minimal waste.
How AI Accelerates Lifecycle Optimization
AI assists in:
-
Predicting polymer aging using digital twins
-
Recommending sustainable fillers and composites
-
Simulating recycling feasibility
-
Forecasting chemical resistance and fatigue
-
Reducing R&D cycles from years to months
As AI adoption increases, businesses that embrace computational polymer development gain unmatched speed and precision in innovation.
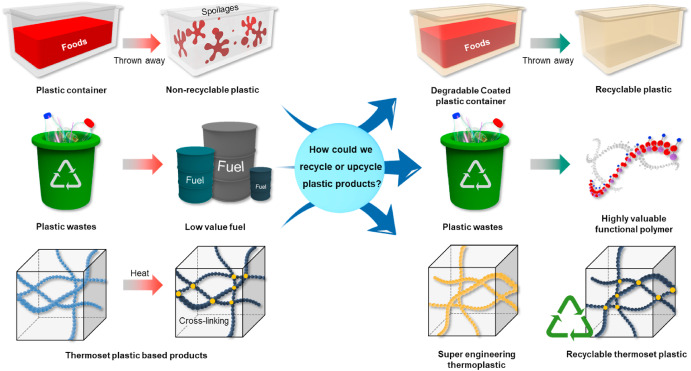
Environmental Impact: Beyond Sustainability Slogans
Sustainability in polymer science is no longer optional; it is a measurable KPI supported by global mandates like EU Green Deal, UN SDGs, and corporate ESG frameworks.
Quantifiable Environmental Contributions
Lifecycle-engineered polymers help:
-
Reduce landfill accumulation
-
Decrease dependency on fossil-based feedstocks
-
Minimize industrial carbon emissions
-
Support efficient energy systems (e.g., EVs, solar tech)
The future belongs to materials engineered with environmental metrics built into their DNA, not added as afterthoughts.
>>> bic white block
Industrial Case Studies: Real-World Transformation
Medical Sector
Self-healing and biocompatible polymers are advancing:
-
Implant durability
-
Tissue-engineering scaffolds
-
Drug-delivery nanocapsules
These solutions reduce surgery repetition rates and improve patient outcomes.
Aerospace and Automotive
Lightweight high-performance polymers replace metals to enhance:
-
Fuel efficiency
-
Thermal stability
-
Corrosion resistance
This shift contributes directly to global decarbonization goals.
Packaging and Consumer Goods
Biodegradable and recyclable polymers reduce single-use plastic waste while maintaining:
-
Food safety
-
Barrier performance
-
Shelf life stability
Key Metrics for Evaluating Advanced Polymers
To deliver next-generation performance, polymers must be evaluated through multi-criteria benchmarking, including:
-
Mechanical strength and fatigue properties
-
Thermal and UV stability
-
Decomposition profile and recyclability index
-
Carbon footprint per lifecycle
-
Regulatory compliance readiness
Companies that track these metrics will position themselves as industry leaders in Engineering Tomorrow’s Materials Today.
Roadmap to Future-Ready Polymer Engineering
| Strategic Focus | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Adopt circular economy manufacturing | Close the materials loop |
| Integrate AI-based polymer R&D | Faster innovation cycles |
| Develop global recycling partnerships | Industrial-scale reprocessing |
| Invest in smart and bio-based polymers | Market leadership in sustainability |
Building a future where technology, nature, and industry coexist demands bold scientific and economic strategies — and polymers sit at the center of that future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What does “polymer lifecycle” mean?
It refers to a polymer’s journey from raw material sourcing to synthesis, manufacturing, product use, and recycling or disposal.
2. Why is lifecycle-based polymer design important?
It improves sustainability, performance, and cost-efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
3. What are the main categories of advanced polymers?
Bio-polymers, smart polymers, nanocomposites, recyclable plastics, and self-healing polymers.
4. How does AI influence polymer engineering?
AI accelerates structure prediction, testing, and optimization, dramatically reducing R&D time.
The future of material science lies Inside the Polymer Lifecycle: Engineering Tomorrow’s Materials Today. By adopting circular strategies, integrating smart design, and leveraging advanced technologies, industries can create high-performance materials while protecting the planet. The journey from polymer creation to sustainable end-of-life pathways is not just scientific progress — it is an ethical and economic necessity.