In recent years, the global demand for Sustainable Polymer Compounds: Innovations in Bio-Based and Recyclable Materials has surged as industries seek eco-friendly solutions without compromising performance. The urgent need to reduce carbon emissions, minimize plastic waste, and preserve natural resources has led scientists and manufacturers to explore innovative bio-based materials and advanced recycling methods.
Sustainable polymer compounds are revolutionizing how we think about plastics. These materials combine renewable feedstocks, enhanced recyclability, and superior mechanical properties — making them ideal for applications in automotive, packaging, construction, and consumer goods. This article explores how innovations in bio-based and recyclable materials are redefining the polymer industry for a circular and sustainable future.
>>> bic cable
What Are Sustainable Polymer Compounds?
Definition and Core Concept
Sustainable polymer compounds are engineered materials designed to minimize environmental impact throughout their life cycle. They are derived from renewable resources (like corn starch, cellulose, or algae) or optimized for recyclability, biodegradability, and energy efficiency during production.
Key Characteristics
-
Derived from bio-based monomers or recycled polymers
-
Maintain or exceed the mechanical strength of traditional plastics
-
Lower carbon footprint and energy consumption
-
Compatible with existing manufacturing technologies
-
Often biodegradable or chemically recyclable
Why They Matter
Traditional plastics, primarily made from fossil fuels, have become a significant source of pollution. Sustainable alternatives address these challenges by reducing dependence on petroleum, improving recyclability, and supporting a circular economy model.
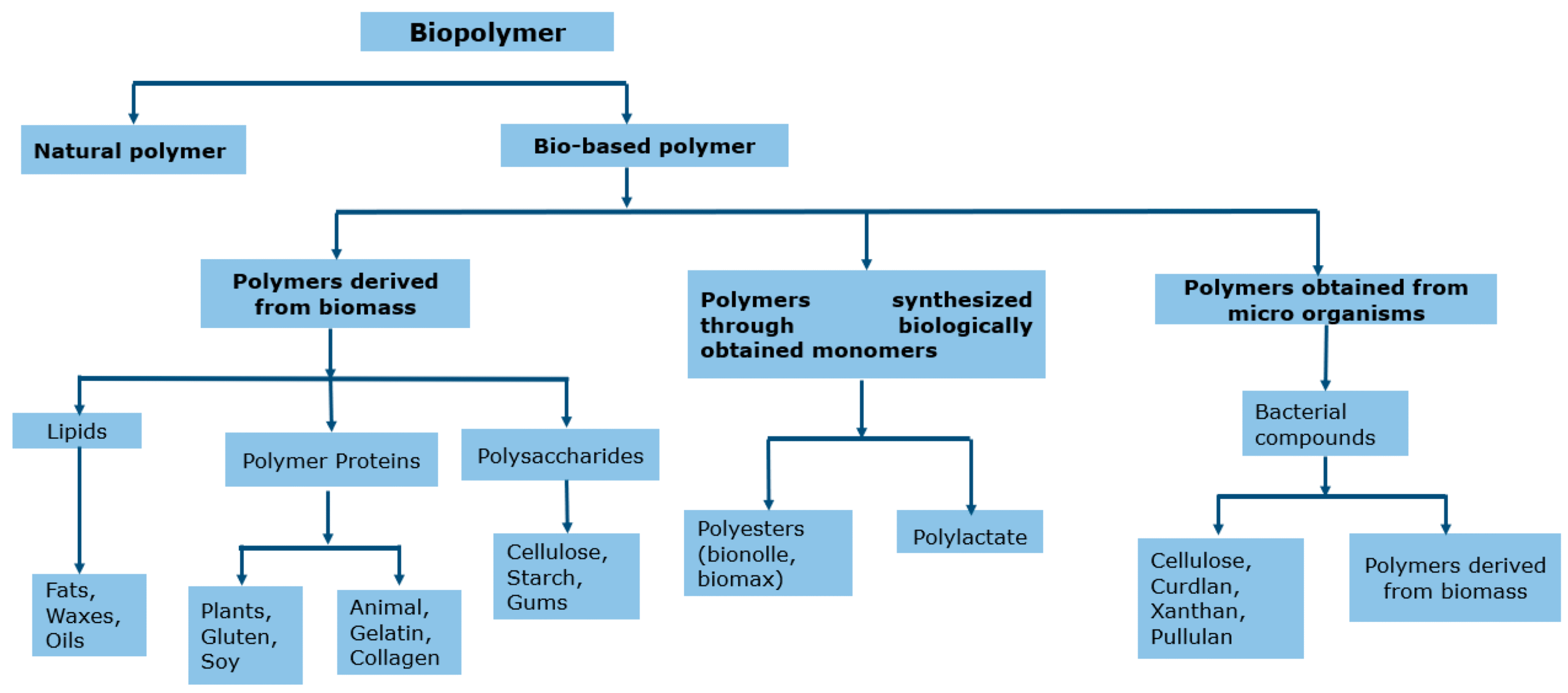
The Science Behind Bio-Based Polymer Innovations
1. Feedstock Revolution
Modern bio-based polymers utilize renewable raw materials such as:
-
Plant oils and sugars (for polyesters and polyurethanes)
-
Lignin and cellulose (for biocomposites)
-
Algae and bacteria (for PHA and PHB bioplastics)
These resources are not only renewable but can be engineered to produce polymers with specific molecular architectures, enabling tailored properties for diverse applications.
2. Green Polymerization Techniques
Recent innovations focus on enzyme-catalyzed and solvent-free polymerization methods, significantly reducing the use of toxic catalysts and solvents. Such approaches ensure that the resulting polymers are environmentally benign throughout production and use.
3. Smart Blending and Compounding
By blending natural polymers (like PLA or PHA) with synthetic recyclables (like PET or PP), researchers achieve hybrid compounds that combine sustainability with durability, flexibility, and heat resistance.
Innovations in Recyclable and Circular Polymer Systems
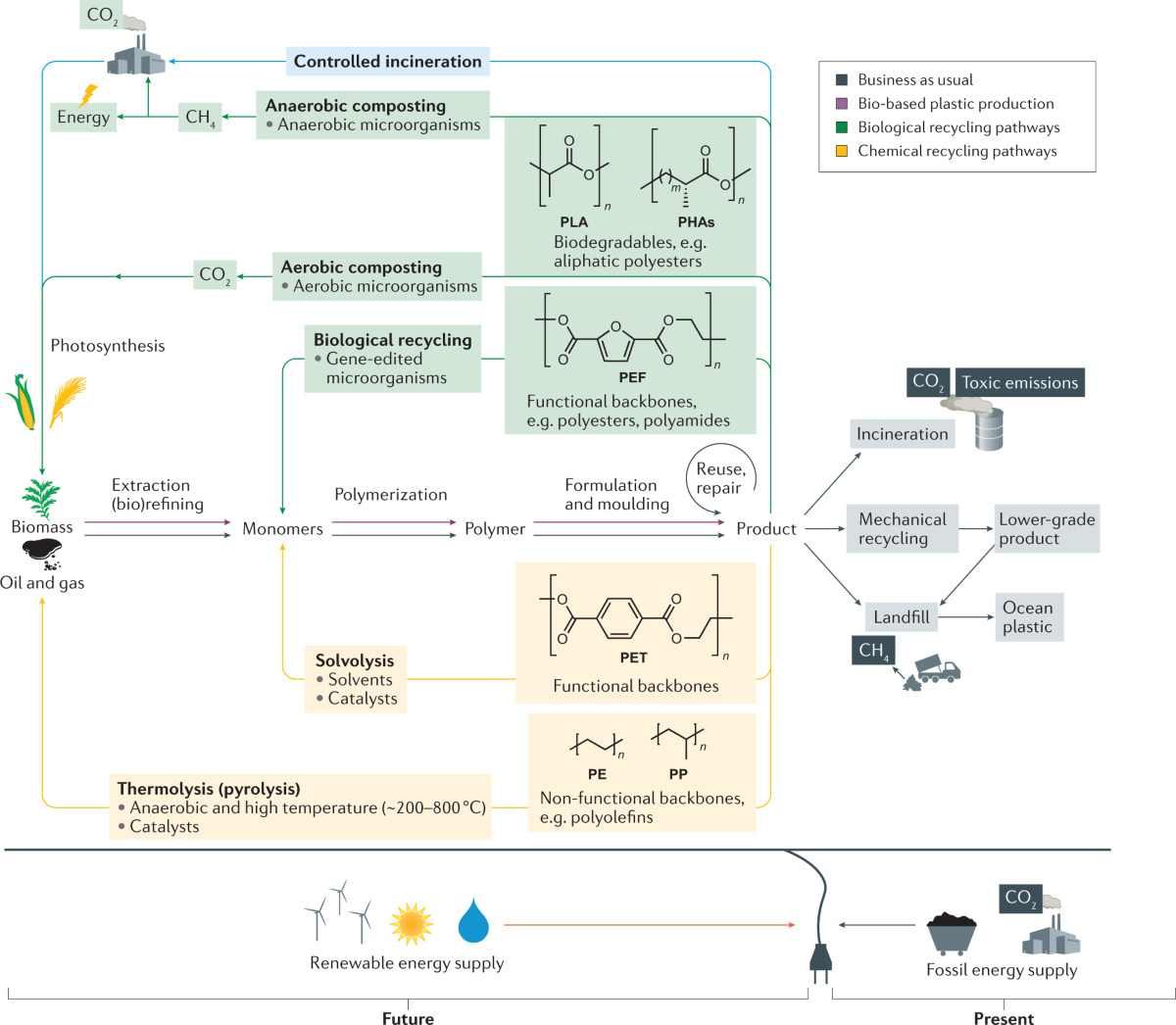
1. Chemical Recycling Breakthroughs
Unlike traditional mechanical recycling, which downgrades material quality, chemical recycling breaks polymers down into their monomer building blocks. These can then be repolymerized into virgin-quality plastics — a game-changer for the circular economy.
2. Advanced Sorting and Tracing Technologies
Innovations in AI-based sorting systems and digital watermarks allow for precise separation of plastic waste streams, enhancing the efficiency and purity of recyclable polymers.
3. Closed-Loop Manufacturing
Major corporations are now adopting closed-loop production systems where waste polymers are continuously reprocessed and reused, drastically cutting down landfill contributions and production costs.
Advantages of Sustainable Polymer Compounds
| Aspect | Traditional Polymers | Sustainable Polymers |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Materials | Petroleum-based | Renewable or recycled sources |
| Environmental Impact | High emissions, non-biodegradable | Low emissions, biodegradable/recyclable |
| Durability | High | Comparable or enhanced |
| Cost (current) | Lower | Slightly higher but decreasing |
| End-of-Life | Landfill or incineration | Compostable or recyclable |
Environmental Benefits
-
Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
-
Decreased reliance on fossil fuels
-
Enhanced waste management efficiency
-
Support for circular economy initiatives
Economic and Industrial Benefits
-
Long-term cost savings through recyclability
-
Enhanced brand value through sustainable credentials
-
Eligibility for green certifications and eco-labels
Challenges and Limitations
Despite the benefits, sustainable polymer compounds face several challenges:
1. Cost and Scalability
Producing bio-based polymers at industrial scale remains more expensive than petroleum-based alternatives. However, advancements in biotechnology and supply chain optimization are rapidly closing this gap.
2. Material Performance Variability
Some bio-based materials exhibit lower thermal stability or moisture sensitivity, limiting their use in high-performance sectors like aerospace or electronics.
3. Recycling Infrastructure
Many regions still lack adequate infrastructure for efficient collection, sorting, and recycling of advanced polymer compounds.
4. Consumer Awareness
The success of sustainable polymers also depends on consumer education — understanding the difference between biodegradable, compostable, and recyclable materials.
>>> bic stone
Key Examples of Sustainable Polymer Innovations
1. Polylactic Acid (PLA)
Derived from corn starch or sugarcane, PLA is one of the most widely used bio-based polymers. It’s biodegradable, transparent, and suitable for packaging, textiles, and 3D printing.
2. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
Produced by microbial fermentation, PHAs are fully biodegradable and compatible with marine environments, making them ideal for single-use items.
3. Recycled PET (rPET)
Through advanced depolymerization, PET bottles can be chemically recycled into high-quality rPET, reducing virgin plastic demand in textiles and packaging.
4. Bio-Based Polyamides
Used in automotive and electronics, bio-polyamides derived from castor oil offer superior strength and heat resistance compared to traditional nylons.
The Role of Sustainable Polymers in Major Industries
1. Automotive Sector
Manufacturers integrate bio-based composites and recyclable polymers for lightweight vehicle parts, reducing emissions and improving fuel efficiency.
2. Packaging Industry
Sustainable polymers like PLA and rPET are transforming packaging — from biodegradable films to compostable containers, replacing single-use plastics.
3. Construction and Electronics
In construction, durable biocomposites reduce environmental impact. In electronics, recyclable housings and insulation materials are improving the sector’s sustainability footprint.
Future Trends in Sustainable Polymer Compounds
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence
AI-driven compounding systems enable precise material design, predicting performance outcomes and optimizing formulations for sustainability and efficiency.
2. 3D Printing with Bio-Based Materials
Additive manufacturing using sustainable polymers like PLA or PHA is becoming a cornerstone of eco-conscious prototyping and production.
3. Regulatory Support and Global Standards
Governments and international organizations are enforcing stricter eco-design standards and plastic reduction policies, driving innovation in sustainable materials.
4. Consumer-Driven Market Evolution
As eco-consciousness grows, brands that adopt sustainable polymer strategies gain stronger market positions and customer trust.
>>> bic tile
Practical Applications and Case Studies
-
Coca-Cola PlantBottle: Made with 30% plant-based materials, showcasing scalable bio-based packaging.
-
Ford Motor Company: Using soy-based foams and biocomposites in car interiors.
-
Adidas Futurecraft Loop: Fully recyclable shoe made from a single polymer type for infinite recyclability.
These examples demonstrate that sustainability is not just a trend — it’s a transformative shift in material science.
>>> bic white block
Conclusion: The Path Toward a Greener Future
The innovations in Sustainable Polymer Compounds: Bio-Based and Recyclable Materials are redefining modern manufacturing. From renewable feedstocks to chemical recycling breakthroughs, the transition toward sustainable materials marks a crucial step in building a circular, low-carbon economy.
As technologies mature and awareness grows, the future belongs to materials that not only perform — but also preserve. Businesses investing today in sustainable polymer R&D will lead tomorrow’s eco-industrial revolution.
Frequently Asked Questions :
1. What are sustainable polymer compounds?
They are advanced materials engineered from renewable or recycled sources, designed to minimize environmental impact while maintaining industrial performance standards.
2. Are bio-based polymers fully biodegradable?
Not always. Some are biodegradable (like PLA or PHA), while others are bio-based but durable, designed for recyclability rather than decomposition.
3. What industries benefit most from sustainable polymers?
Automotive, packaging, construction, electronics, and consumer goods are major beneficiaries, leveraging these materials for eco-friendly innovation.
4. Are sustainable polymers more expensive?
Currently, production costs are higher, but economies of scale and technological advances are rapidly making them competitive with traditional plastics.